
Technology and the Universities of Tomorrow
20.09.2023 - 03:20
In partnership with the Coalition for Digital Learners, Mandala explored the role of technology in higher education. We conducted a student-centric survey alongside economic modeling of how Australian universities can leverage technology to deliver better teaching, better student outcomes, and a stronger economy.
In partnership with the Coalition for Digital Learners, Mandala explored the role of technology in higher education.
This research examines the changing role of technology in universities and identifies how we could improve the performance of Australian universities and grow our economy by more than $3 billion a year.
Technology is core to the way teaching and learning is conducted today. As we consider how to strengthen universities and to be more inclusive of students from a broader range of backgrounds in the future, the position and potential of technology must be at the centre of our policy thinking.
Technology is rapidly changing university learning – and more change is coming
New technologies have transformed higher education in the past 30 years – from the advent of the internet to the use of tablets and mobile learning technologies. At each stage, universities, students and regulators have reacted and adapted to these changes. Today, students have wide availability of technologies at their disposal to support their education. This ranges from learning management software, such as Canvas, to mass open online courses (MOOCs), such as Khan Academy.
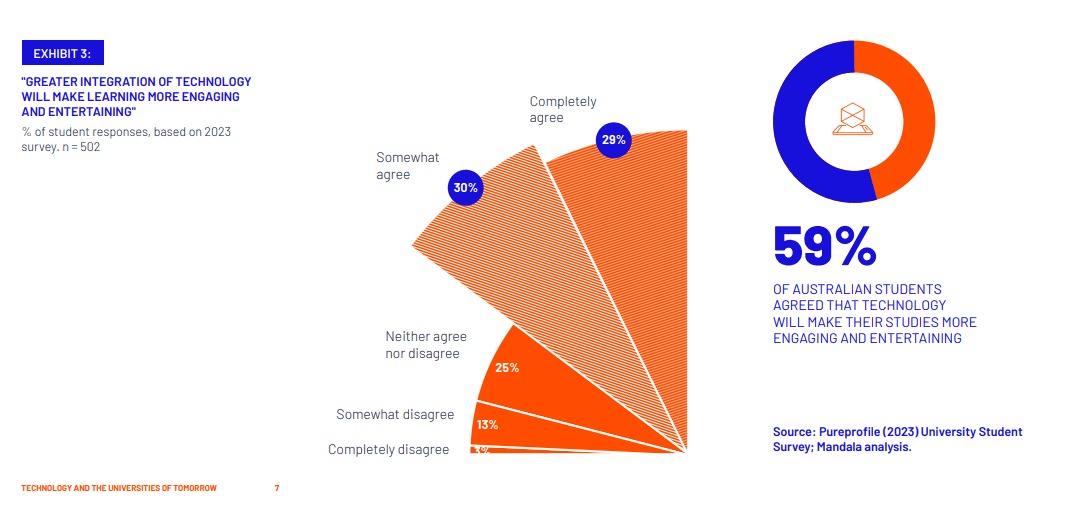
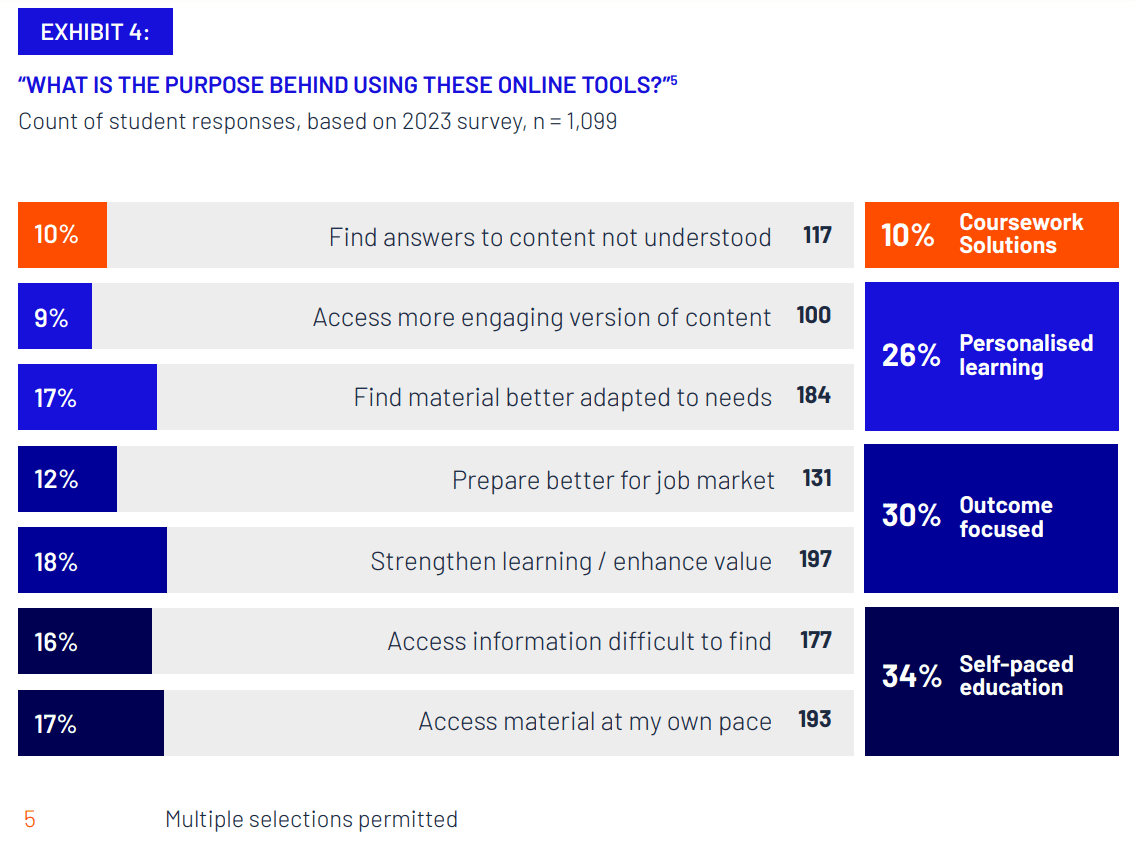
Students overwhelmingly use technology ethically and effectively
Our survey shows that most university students are using technology as supplementary tools to help them succeed in their studies – not for academically dishonest reasons.
90 per cent of students use online education tools to help them learn at their own pace, enhance their learning experience, or to make their learning more personalised and engaging. Technology provided by universities and sourced independently by students are commonly used by students of all ages and backgrounds. Just 10 per cent of students reported using technology to help them access answers to homework or exam material that they did not understand. Moreover, while this small cohort may include some with unethical motivations, it also includes students driven by a genuine desire to comprehend course material.
Technology benefits students from diverse backgrounds the most
Our survey shows students from diverse backgrounds – including those from lower socio-economic areas, those who don’t speak English as a first language, those caring for others, or those balancing study with work responsibilities – place greater importance on the flexibility and support that education technology tools offer to help them succeed in their studies.
Australian universities lag on equity, student centricity, and economic outcomes
Australia is currently lagging on the core objective of improving university participation and completion rates for people from underrepresented groups. Students from low socio-economic backgrounds make up just 16 per cent of domestic enrolments – missing the target of 20 per cent set by the Bradley Review – while less than 65 per cent of students from low socio-economic backgrounds are completing their degrees. The Universities Accord process presents major challenges to the current context, by setting ambitious future targets for the engagement of diverse and equitable groups in university education.
Improving university performance through technology could growth the economy by more than $3 billion per year
Our modelling indicates that growing Australia’s education technology sector in partnership with universities, as well as improving the application of technology in university learning, could have widespread economic benefits. To achieve this outcome, we need a range of regulatory reforms as well as a closer links between universities, industry and the Australian EdTech sector.
Read our latest posts

The Fragmentation Tax
Australian retailers operate across a patchwork of inconsistent state and territory regulations that, left unchecked, will cost the economy $26 billion and households $9.4 billion over the next decade. Commissioned by the Australian Retail Council, this Mandala report finds that regulatory fragmentation in retail - Australia's second-largest employer, generating $649 billion in economic activity annually - is compounding the country's productivity crisis at the worst possible time. The report identifies specific issues in transport and logistics, and packaging and waste as priority areas for reform, where harmonisation alone would inject up to $1.65 billion into the economy over 10 years. It recommends the Federal Government use its National Competition Policy framework to drive reform - including a $260 million increase to the National Productivity Fund, a new National Harmonisation Council, and a mandate that Regulatory Impact Statements explicitly quantify fragmentation risks.
23 Feb, 2026

Reforming Victoria's Windfall Gains Tax
Victoria's Windfall Gains Tax (WGT), introduced in July 2023, has compounded a decade of new and increased property taxes that have made Melbourne the most costly major city in Australia for development. Commissioned by the Property Council Victoria, this Mandala report finds that developer taxes and charges now account for 18% of total costs on Melbourne developments - double the rate of Sydney - and that the average WGT liability pushes project returns below the viability threshold. The analysis estimates that removing the WGT could unlock $1.4 billion in additional annual investment, support 2,700 jobs and deliver the equivalent of 3,100 new homes per year by 2030. The report also presents a suite of targeted reforms across financial relief, predictability, and policy alignment that would restore investor confidence while balancing the government's revenue objectives.
23 Feb, 2026

Restoring affordable access to specialist care in Australia
In this report, Mandala and Private Healthcare Australia (PHA) studied the affordability of specialist care in Australia. We find that specialist fees are rising, exacerbating cost-of-living pressures on consumers and worsening the affordability of healthcare. We propose a targeted package of measures to improve consumers' ability to access high-quality care, of their choosing, at fair and transparent costs.
3 Feb, 2026

Critical Minerals Strategic Reserve Design
Mandala's latest report for the Association of Mining and Exploration Companies (AMEC) sets out an industry-informed approach to implementing Australia’s Critical Minerals Strategic Reserve, with a focus on rare earths critical to national security and the energy transition. Bringing together 10 Australian rare earth developers, and drawing on international precedents and economic analysis, the report recommends a commercially viable and fiscally sustainable model to support new investment in Australia’s rare earths sector while managing risk to taxpayers.
12 Jan, 2026